The reach of imperialism answer key – Embark on an illuminating journey with our comprehensive reach of imperialism answer key, meticulously crafted to unravel the intricate tapestry of imperialism’s origins, methods, impacts, and enduring legacy. Immerse yourself in a narrative that seamlessly blends historical depth with contemporary relevance, unraveling the profound influence of imperialism on the shaping of our world.
Through this comprehensive guide, we delve into the historical roots of imperialism, tracing its evolution from its earliest manifestations to its far-reaching global impact. We dissect the key factors that fueled imperial expansion, exploring the motivations and strategies employed by major imperial powers.
Moreover, we illuminate the diverse methods of imperial control, from military force and economic exploitation to cultural assimilation, providing vivid examples of their implementation.
Historical Overview of Imperialism’s Reach
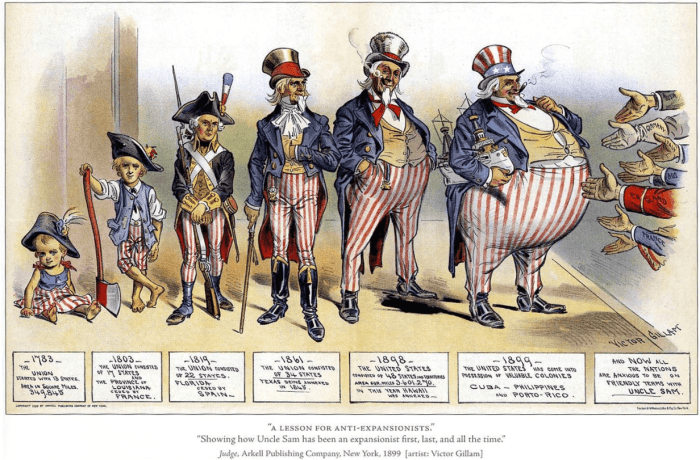
Imperialism, a system of domination in which one country exerts political, economic, and military control over other territories, has a long and complex history. Its origins can be traced back to the 15th century, when European powers began to explore and colonize the Americas, Africa, and Asia.The
key factors that drove imperial expansion included the search for new markets, resources, and strategic advantages. European powers competed fiercely for control of these territories, often leading to conflict and war. By the late 19th century, several major imperial powers had emerged, including Great Britain, France, Germany, and the United States.
These powers established vast empires that spanned the globe, encompassing hundreds of millions of people.
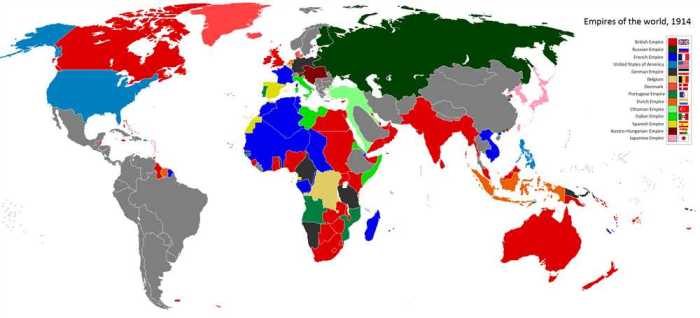
Major Imperial Powers and Their Empires
-
-*Great Britain
The British Empire was the largest empire in history, covering over 13 million square kilometers at its peak. It included territories in North America, Africa, Asia, and Oceania.
-*France
The French Empire was the second largest empire, covering over 11 million square kilometers. It included territories in North Africa, West Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Caribbean.
-*Germany
The German Empire was a relatively short-lived empire, but it was one of the most powerful in Europe. It included territories in Central Europe, Africa, and the Pacific.
-*United States
The American Empire was founded in the late 19th century and grew rapidly through the acquisition of territories in the Pacific and the Caribbean. It also established protectorates in Central America and the Middle East.
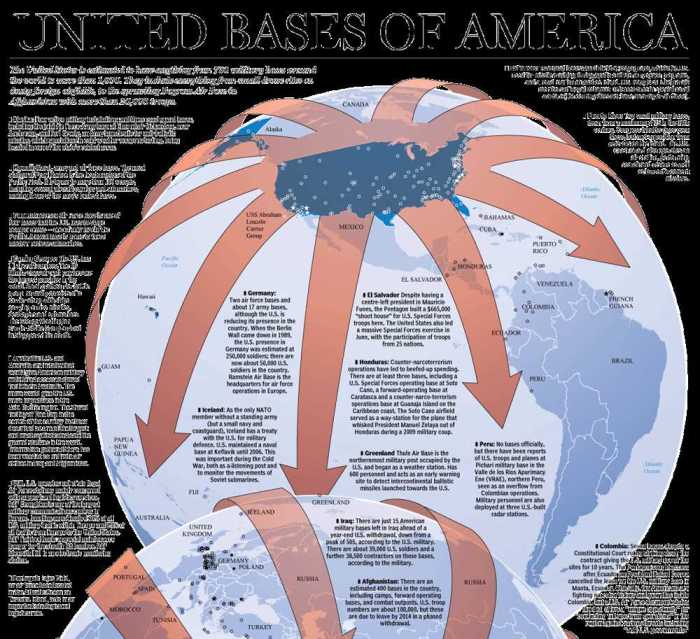
Methods of Imperial Control
Imperial powers employed a range of political, economic, and cultural mechanisms to establish and maintain control over their colonies. These methods aimed to secure political authority, exploit economic resources, and shape cultural identities in ways that benefited the imperial power.
Military Force
Military force played a crucial role in imperial expansion. Imperial powers used their superior military might to conquer and subdue territories, often through violent campaigns of invasion and occupation. Military force was also used to suppress resistance and maintain order within colonies.
Economic Exploitation, The reach of imperialism answer key
Imperial powers exploited the economic resources of their colonies to fuel their own economies. This included extracting raw materials, establishing plantations, and imposing trade monopolies. Economic policies were designed to maximize profits for the imperial power, often at the expense of local populations.
Cultural Assimilation
Imperial powers often sought to assimilate the cultures of their colonies into their own. This involved imposing their language, religion, and values on colonized populations. Cultural assimilation aimed to create a sense of loyalty to the imperial power and to suppress local cultural traditions and identities.
Examples of Imperial Policies and Practices
- British Raj in India: The British established direct rule over India, exploiting its vast resources and imposing their own administrative and legal systems.
- French colonization of Algeria: France conquered and colonized Algeria, suppressing local resistance and establishing a settler colonial regime.
- Dutch East India Company in Indonesia: The Dutch East India Company established a commercial empire in Indonesia, exploiting its spice trade and imposing a monopoly on the nutmeg industry.
Impact of Imperialism on Colonized Societies

Imperialism profoundly impacted colonized societies, leaving lasting social, economic, and political consequences. The imposition of foreign rule led to forced labor, resource extraction, and cultural suppression, which had devastating effects on local populations.
Social Consequences
- Disruption of Traditional Societies:Imperial powers often disrupted existing social structures, replacing local customs and practices with their own. This led to a loss of cultural identity and social cohesion.
- Forced Labor:Colonizers often used forced labor to extract resources and build infrastructure. This practice subjected local populations to harsh working conditions and exploitation.
- Racial Segregation:Imperial powers often established systems of racial segregation, creating divisions between colonizers and colonized peoples. This discrimination extended to education, housing, and employment opportunities.
Economic Consequences
- Resource Extraction:Imperial powers extracted vast quantities of natural resources from colonized territories, often depleting local resources and damaging the environment.
- Dependency on Foreign Goods:Colonizers often disrupted local economies by flooding markets with cheap imported goods, undermining local industries and creating dependency.
- Exploitation of Labor:Colonizers often exploited local labor for low wages, leading to poverty and inequality.
Political Consequences
- Loss of Independence:Imperialism resulted in the loss of political independence for colonized territories, which were subjected to foreign rule and exploitation.
- Suppression of Dissent:Colonizers often suppressed dissent and political opposition through censorship, imprisonment, and violence.
- Legacy of Conflict:The political divisions and grievances created by imperialism often persisted after independence, leading to ongoing conflict and instability.
Resistance Movements
Despite the challenges, colonized peoples resisted imperial rule through various means. Resistance movements included:
- Armed Rebellions:In some cases, colonized peoples engaged in armed resistance against imperial powers.
- Nonviolent Protests:Others employed nonviolent protests, such as boycotts, strikes, and civil disobedience.
- Cultural Resistance:Colonized peoples often preserved their cultural identity and traditions through art, music, and literature.
These resistance movements played a crucial role in the eventual struggles for independence and the dismantling of colonial empires.
Legacy of Imperialism: The Reach Of Imperialism Answer Key
Imperialism has left a profound and enduring impact on the world. The geopolitical, economic, and cultural legacies of colonial rule continue to shape global affairs today.
One of the most significant legacies of imperialism is the creation of nation-states. European powers arbitrarily divided up the world into colonies, often with little regard for the ethnic or cultural makeup of the people living there. This has led to ongoing conflicts and tensions between different groups, as well as the formation of artificial borders that do not reflect the natural distribution of populations.
Imperialism also had a devastating impact on the economies of colonized countries. European powers plundered resources, disrupted traditional trade networks, and imposed economic policies that benefited the colonizers at the expense of the local population. This led to widespread poverty and underdevelopment, which continue to plague many former colonies today.
Finally, imperialism has had a profound impact on the cultures of colonized peoples. European powers often sought to suppress or assimilate indigenous cultures, leading to the loss of languages, traditions, and beliefs. This cultural imperialism has had a lasting impact on the identities of colonized peoples, and continues to be a source of tension and conflict in many parts of the world.
Post-colonial Challenges and Opportunities
The legacy of imperialism continues to present challenges and opportunities for post-colonial societies. One of the most pressing challenges is the need to overcome the economic and social inequalities that were created by colonial rule. Many former colonies are still struggling to develop their economies and provide basic services to their populations.
Another challenge is the need to address the psychological and cultural legacy of imperialism. Many post-colonial societies are still grappling with the effects of colonialism on their identities and sense of self-worth. This can lead to feelings of inferiority and dependency, as well as a lack of confidence in the ability to chart their own course in the world.
However, there are also opportunities that come with post-colonialism. Many former colonies have gained independence and are now able to determine their own futures. They have the opportunity to build new societies that are based on their own values and traditions.
They also have the opportunity to learn from the mistakes of the past and to avoid the pitfalls of imperialism.
The legacy of imperialism is a complex and challenging one. However, it is also a legacy of opportunity. Post-colonial societies have the opportunity to overcome the challenges of the past and to build a better future for themselves.
Detailed FAQs
What are the key factors that drove imperial expansion?
Economic motives, political ambitions, technological advancements, and the search for resources were among the primary factors.
How did imperial powers maintain control over their colonies?
Through a combination of military force, economic exploitation, cultural assimilation, and administrative structures.
What were the social consequences of imperialism for colonized peoples?
Forced labor, resource extraction, cultural suppression, and social hierarchies were among the devastating social impacts.
How does imperialism continue to impact the world today?
Its legacy can be seen in geopolitical boundaries, economic disparities, cultural influences, and ongoing post-colonial challenges.