Psychology exam 1 chapters 1-3 – Psychology Exam 1: Chapters 1-3 embarks on an intriguing journey into the fascinating realm of psychology. This comprehensive exploration unveils the fundamental concepts and principles that underpin this captivating field, providing a solid foundation for your understanding of human behavior and mental processes.
Prepare to delve into the intricate workings of the human mind as we navigate the essential chapters, exploring the scientific method in psychology, the biological bases of behavior, and the captivating world of sensation and perception.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. It encompasses a broad range of topics, from the biological basis of behavior to the social and cultural influences on our thoughts and actions. Psychological research has applications in various fields, including education, healthcare, and business.
There are many different psychological perspectives, each with its own unique assumptions about the nature of the human mind and behavior. Some of the most common perspectives include:
- The psychodynamic perspective focuses on the unconscious mind and the role of early childhood experiences in shaping personality and behavior.
- The behavioral perspective focuses on observable behavior and the role of learning in shaping behavior.
- The cognitive perspective focuses on mental processes, such as thinking, memory, and language.
- The humanistic perspective focuses on the individual’s subjective experience and the importance of personal growth.
- The biological perspective focuses on the biological basis of behavior, including the role of genes, hormones, and brain structures.
The scientific method is a systematic approach to research that is used by psychologists to test hypotheses and theories. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Formulating a hypothesis
- Designing a study to test the hypothesis
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the data
- Drawing conclusions
The scientific method is an important tool for psychologists because it allows them to test their theories and hypotheses in a systematic and objective way.
Chapter 2: Biological Bases of Behavior
Psychology is not only about the mind, but also about the brain and body. This chapter explores the biological foundations of behavior, including the structure and function of the nervous system, the role of neurotransmitters in behavior, and the influence of genetics on behavior.
Structure and Function of the Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex network of specialized cells that communicates information throughout the body. It consists of two main divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is the center of the nervous system and controls all bodily functions, including thought, emotion, and movement. The spinal cord is a long, thin bundle of nerves that connects the brain to the rest of the body.
The PNS consists of all the nerves that extend from the CNS to the rest of the body. These nerves carry sensory information from the body to the brain and motor commands from the brain to the muscles and glands.
Role of Neurotransmitters in Behavior
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between neurons. They play a crucial role in regulating a wide range of behaviors, including mood, sleep, and appetite.
There are many different neurotransmitters, each with its own unique function. For example, serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is involved in regulating mood and sleep. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is involved in regulating movement and reward.
Influence of Genetics on Behavior
Genetics plays a role in shaping our behavior. Our genes influence our physical characteristics, such as our height and eye color, as well as our psychological traits, such as our personality and intelligence.
The psychology exam 1 chapters 1-3 covers a wide range of topics, including the history of psychology, research methods, and the major theoretical perspectives. As you study for the exam, it’s important to keep in mind the ancient dictum in real estate : “location, location, location.”
In other words, the key to success on the exam is to focus on the most important concepts and theories. By doing so, you’ll be able to answer the questions on the exam with confidence and accuracy.
However, it is important to note that genetics is not the only factor that influences behavior. Environmental factors, such as our upbringing and experiences, also play a role.
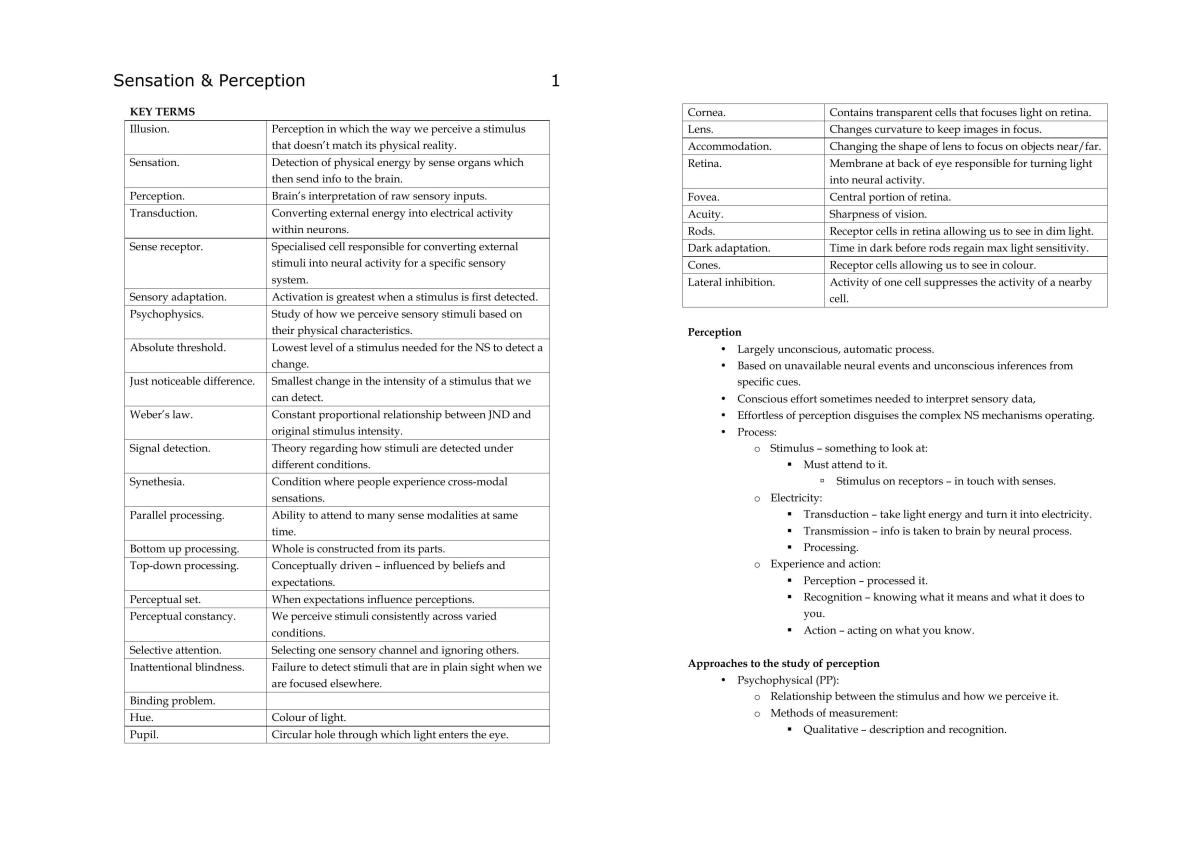
Chapter 3: Sensation and Perception: Psychology Exam 1 Chapters 1-3
Sensation and perception are two interconnected processes that allow us to experience the world around us. Sensation is the process of detecting physical stimuli from the environment through our sensory receptors, while perception is the process of interpreting and organizing these sensations to create a meaningful experience of the world.
Sensation, Psychology exam 1 chapters 1-3
Sensation begins with sensory receptors, which are specialized cells that respond to specific types of physical stimuli. These receptors convert the physical stimuli into electrical signals that are then sent to the brain. The brain then interprets these signals to create a sensation.
- Types of sensory receptors:There are many different types of sensory receptors, each of which responds to a specific type of physical stimulus. For example, photoreceptors in the eyes respond to light, while thermoreceptors in the skin respond to heat and cold.
- Sensory thresholds:The ability of a sensory receptor to detect a stimulus depends on the strength of the stimulus. The minimum amount of stimulus energy that can be detected is called the absolute threshold.
- Sensory adaptation:Sensory receptors adapt to constant stimuli over time, meaning that we become less sensitive to them. This is why we can’t always smell a strong odor after a while, or why we can’t feel the pressure of our clothes on our skin after a while.
Perception
Perception is the process of interpreting and organizing sensations to create a meaningful experience of the world. Perception is influenced by a number of factors, including our expectations, beliefs, and past experiences.
- Types of perception:There are many different types of perception, including visual perception, auditory perception, and tactile perception. Each type of perception involves a different set of sensory receptors and a different set of brain processes.
- Perceptual organization:The brain organizes sensations into meaningful patterns. For example, we perceive a face as a face, even though it is made up of many different features. This is because the brain has learned to group together the features that make up a face.
- Perceptual illusions:Perceptual illusions are errors in perception that occur when the brain misinterprets sensory information. For example, the Müller-Lyer illusion makes two lines of equal length appear to be different lengths.
Factors that Influence Perception
Perception is influenced by a number of factors, including:
- Attention:We are more likely to perceive things that we are paying attention to. For example, if you are looking for a specific person in a crowd, you are more likely to notice them than if you are not paying attention to them.
- Motivation:Our motivations can also influence our perception. For example, if you are hungry, you are more likely to perceive food as being more appealing than if you are not hungry.
- Expectations:Our expectations can also influence our perception. For example, if you expect to see a certain thing, you are more likely to perceive it, even if it is not actually there.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the scope of psychology?
Psychology encompasses a broad range of topics, including the study of human behavior, mental processes, and cognitive functions. It explores how individuals interact with their environment, develop over time, and navigate various challenges and opportunities.
How does the scientific method apply to psychology?
The scientific method is a systematic approach used in psychology to gather and analyze data, test hypotheses, and draw conclusions. It involves formulating research questions, designing experiments, collecting and analyzing data, and interpreting the results.
What role do neurotransmitters play in behavior?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons in the nervous system. They influence a wide range of behaviors, including mood, cognition, and movement. Understanding their function is crucial for comprehending the biological basis of behavior.
