Divide the compounds below into meso or non-meso compounds – In the realm of stereochemistry, distinguishing between meso and non-meso compounds is crucial for understanding their properties and reactivities. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the concept, methods for classification, and applications of meso and non-meso compounds.
Meso compounds possess an internal plane of symmetry, rendering them achiral and optically inactive. Conversely, non-meso compounds lack such symmetry, resulting in chirality and optical activity.
1. Identifying Meso and Non-Meso Compounds
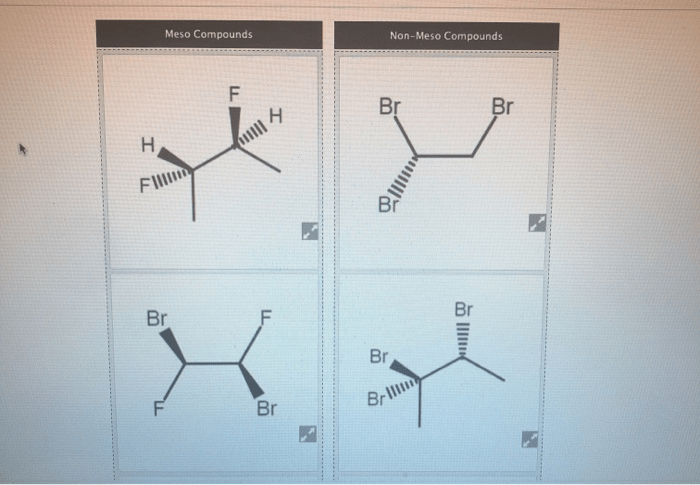
Meso compounds are achiral compounds that contain at least one chiral center but have an internal plane of symmetry that bisects the molecule and makes it superimposable on its mirror image. Non-meso compounds, on the other hand, are chiral compounds that lack an internal plane of symmetry and are not superimposable on their mirror images.
For example, 2,3-dibromobutane is a meso compound because it has a chiral center but also has an internal plane of symmetry that bisects the molecule. On the other hand, 2-bromobutane is a non-meso compound because it has a chiral center but lacks an internal plane of symmetry.
The structural features that differentiate meso and non-meso compounds are the presence or absence of an internal plane of symmetry. Meso compounds have an internal plane of symmetry, while non-meso compounds do not.
2. Methods for Classifying Meso and Non-Meso Compounds
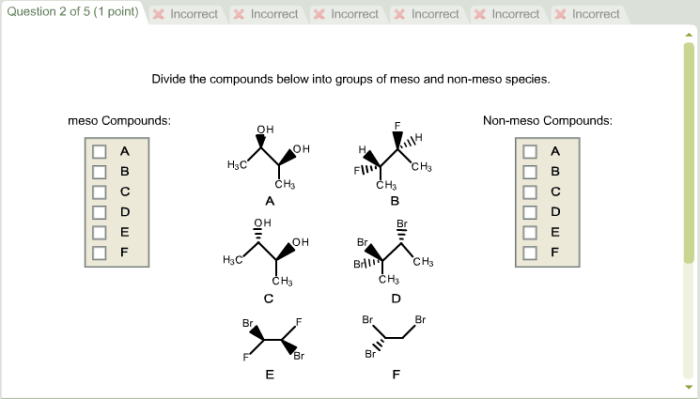
Meso and non-meso compounds can be classified using various methods, including symmetry and the presence of chiral centers.
Symmetry
Symmetry is a powerful tool for identifying meso and non-meso compounds. A molecule is meso if it has an internal plane of symmetry. A molecule is non-meso if it lacks an internal plane of symmetry.
Plane of Symmetry Rule, Divide the compounds below into meso or non-meso compounds
The plane of symmetry rule states that a molecule is meso if it has an internal plane of symmetry that bisects all of the bonds to the chiral centers. If a molecule has an internal plane of symmetry that does not bisect all of the bonds to the chiral centers, then the molecule is non-meso.
Chiral Centers
The presence of chiral centers can also be used to classify meso and non-meso compounds. A molecule is non-meso if it contains one or more chiral centers. A molecule is meso if it contains one or more chiral centers, but the molecule has an internal plane of symmetry that bisects all of the bonds to the chiral centers.
3. Applications of Meso and Non-Meso Compounds
Meso and non-meso compounds have different properties and reactivities, which make them useful for a variety of applications.
Meso compounds are often used as chiral building blocks in the synthesis of complex organic molecules. They are also used as chiral solvents and reagents in asymmetric synthesis.
Non-meso compounds are often used as chiral drugs and agrochemicals. They are also used as chiral catalysts and chiral resolving agents.
Meso compounds play an important role in biological systems. For example, meso-tartaric acid is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle.
4. Creating a Table of Meso and Non-Meso Compounds: Divide The Compounds Below Into Meso Or Non-meso Compounds
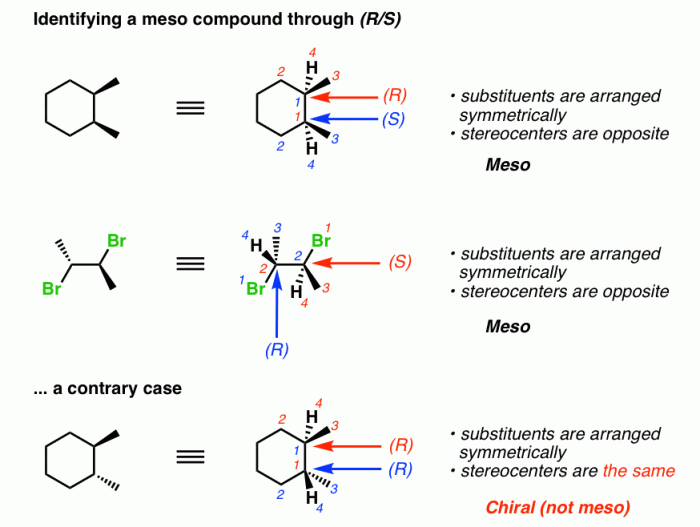
The following table organizes the classification of compounds as meso or non-meso:
| Compound Name | Structure | Symmetry | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2,3-dibromobutane | CH3CHBrCHBrCH3 | Yes | Meso |
| 2-bromobutane | CH3CH2CHBrCH3 | No | Non-meso |
| 2-butanol | CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3 | Yes | Meso |
| 1-butanol | CH3CH2CH2CH2OH | No | Non-meso |
FAQ Overview
What is the key difference between meso and non-meso compounds?
Meso compounds possess an internal plane of symmetry, making them achiral and optically inactive, while non-meso compounds lack such symmetry and are chiral and optically active.
How can I determine if a compound is meso or non-meso?
One method is to examine the compound’s molecular structure for a plane of symmetry. If a plane of symmetry is present, the compound is meso; otherwise, it is non-meso.
What are some examples of meso and non-meso compounds?
Examples of meso compounds include tartaric acid and 2,3-dibromobutane. Examples of non-meso compounds include lactic acid and 2-chlorobutane.