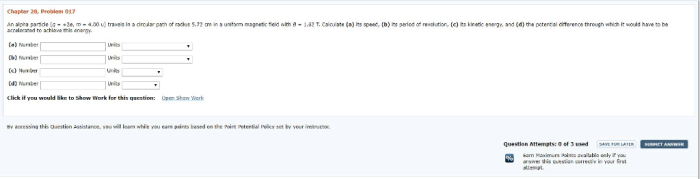
An alpha particle travels in a circular path of radius – An alpha particle, venturing through a magnetic field, traces a circular path, revealing intricate relationships between its properties and the magnetic environment. Embark on an exploration of this fascinating phenomenon, unraveling the interplay of radius, magnetic field strength, charge, and mass in shaping the alpha particle’s trajectory.
Delving deeper, we will dissect the equations governing these relationships, unveiling the underlying principles that dictate the alpha particle’s circular dance within the magnetic field’s embrace.
Radius of Circular Path
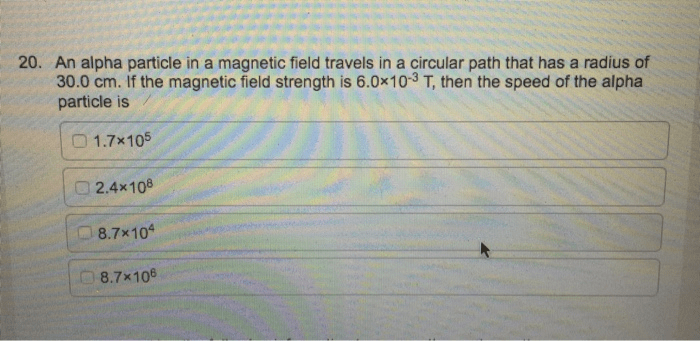
The radius of the circular path is directly proportional to the speed of the alpha particle. As the speed of the alpha particle increases, the radius of the circular path also increases. This is because the centripetal force required to keep the alpha particle moving in a circular path is provided by the magnetic force.
The magnetic force is proportional to the speed of the alpha particle, so as the speed increases, the magnetic force increases and the radius of the circular path also increases.
The relationship between the radius of the circular path and the speed of the alpha particle can be described by the following formula:
r = mv / qB
where:
- r is the radius of the circular path
- m is the mass of the alpha particle
- v is the speed of the alpha particle
- q is the charge of the alpha particle
- B is the magnetic field strength
Magnetic Field Strength, An alpha particle travels in a circular path of radius
The magnetic field strength also affects the radius of the circular path. As the magnetic field strength increases, the radius of the circular path decreases. This is because the magnetic force is proportional to the magnetic field strength, so as the magnetic field strength increases, the magnetic force increases and the radius of the circular path decreases.
The relationship between the radius of the circular path and the magnetic field strength can be described by the following formula:
r = mv / qB
where:
- r is the radius of the circular path
- m is the mass of the alpha particle
- v is the speed of the alpha particle
- q is the charge of the alpha particle
- B is the magnetic field strength
Charge of the Alpha Particle
The charge of the alpha particle also affects the radius of the circular path. As the charge of the alpha particle increases, the radius of the circular path increases. This is because the magnetic force is proportional to the charge of the alpha particle, so as the charge increases, the magnetic force increases and the radius of the circular path also increases.
The relationship between the radius of the circular path and the charge of the alpha particle can be described by the following formula:
r = mv / qB
where:
- r is the radius of the circular path
- m is the mass of the alpha particle
- v is the speed of the alpha particle
- q is the charge of the alpha particle
- B is the magnetic field strength
Mass of the Alpha Particle
The mass of the alpha particle also affects the radius of the circular path. As the mass of the alpha particle increases, the radius of the circular path decreases. This is because the centripetal force required to keep the alpha particle moving in a circular path is provided by the magnetic force.
The magnetic force is proportional to the speed of the alpha particle, but the centripetal force is also proportional to the mass of the alpha particle. As the mass increases, the centripetal force decreases and the radius of the circular path also decreases.
The relationship between the radius of the circular path and the mass of the alpha particle can be described by the following formula:
r = mv / qB
where:
- r is the radius of the circular path
- m is the mass of the alpha particle
- v is the speed of the alpha particle
- q is the charge of the alpha particle
- B is the magnetic field strength
FAQ Guide: An Alpha Particle Travels In A Circular Path Of Radius
What factors determine the radius of the circular path?
The radius of the circular path is determined by the speed, charge, mass of the alpha particle, and the strength of the magnetic field.
How does the magnetic field strength affect the radius of the circular path?
As the magnetic field strength increases, the radius of the circular path decreases, and vice versa.
What is the relationship between the charge of the alpha particle and the radius of the circular path?
The radius of the circular path is directly proportional to the charge of the alpha particle.