Cleft lip repair CPT code plays a crucial role in ensuring appropriate billing and reimbursement for this essential surgical procedure. This article delves into the specifics of the CPT code, its components, and the billing process, providing a comprehensive guide for healthcare professionals.
The CPT code for cleft lip repair is a unique identifier assigned to the procedure, allowing for accurate billing and tracking. Understanding the structure and components of the CPT code is essential for accurate claim submission.
Introduction
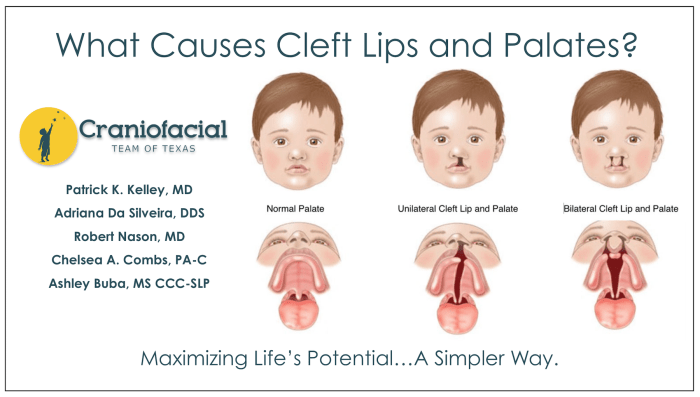
Cleft lip repair is a surgical procedure that aims to correct a cleft lip, a birth defect characterized by a separation in the upper lip.
Cleft lip occurs when the tissues that make up the lip do not fuse together properly during pregnancy. This can result in a small notch in the lip or a complete separation extending into the nose.
Prevalence and Demographics
Cleft lip is a relatively common birth defect, affecting approximately 1 in 700 live births worldwide.
To find the right cleft lip repair CPT code, it’s helpful to have a comprehensive resource like the unit 5 review answer key . This resource provides a detailed overview of the different codes used for cleft lip repair procedures, making it easier to ensure accurate billing.
It is more common in certain populations, such as those of Asian and Native American descent.
CPT Code for Cleft Lip Repair: Cleft Lip Repair Cpt Code
Specific CPT Code
The specific CPT code for cleft lip repair is 40400.
Structure and Components
The CPT code for cleft lip repair is a five-digit code that consists of three components:
- Category code:The first digit (4) indicates that the procedure is a surgery.
- Subcategory code:The second and third digits (04) indicate that the surgery is a repair of the lip.
- Modifier code:The fourth and fifth digits (00) indicate that the surgery is a primary repair.
Billing and Reimbursement
Billing for cleft lip repair using the CPT code is a straightforward process. The surgeon or healthcare provider will submit a claim to the patient’s insurance company, including the CPT code and other relevant information.
The reimbursement rate for cleft lip repair varies depending on the complexity of the procedure, the geographic location, and the insurance company. Typically, reimbursement rates range from $2,000 to $5,000.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
There are a few potential challenges or considerations when billing for cleft lip repair:
- Insurance coverage:Some insurance companies may not cover cleft lip repair, or they may only cover a portion of the cost. It is important to check with the patient’s insurance company before performing the procedure to ensure that it will be covered.
- Coding errors:Using the incorrect CPT code or submitting incomplete or inaccurate information can lead to denied claims. It is important to carefully review the claim before submitting it.
- Payment delays:Insurance companies can take several weeks or even months to process claims. This can lead to delays in payment for the surgeon or healthcare provider.
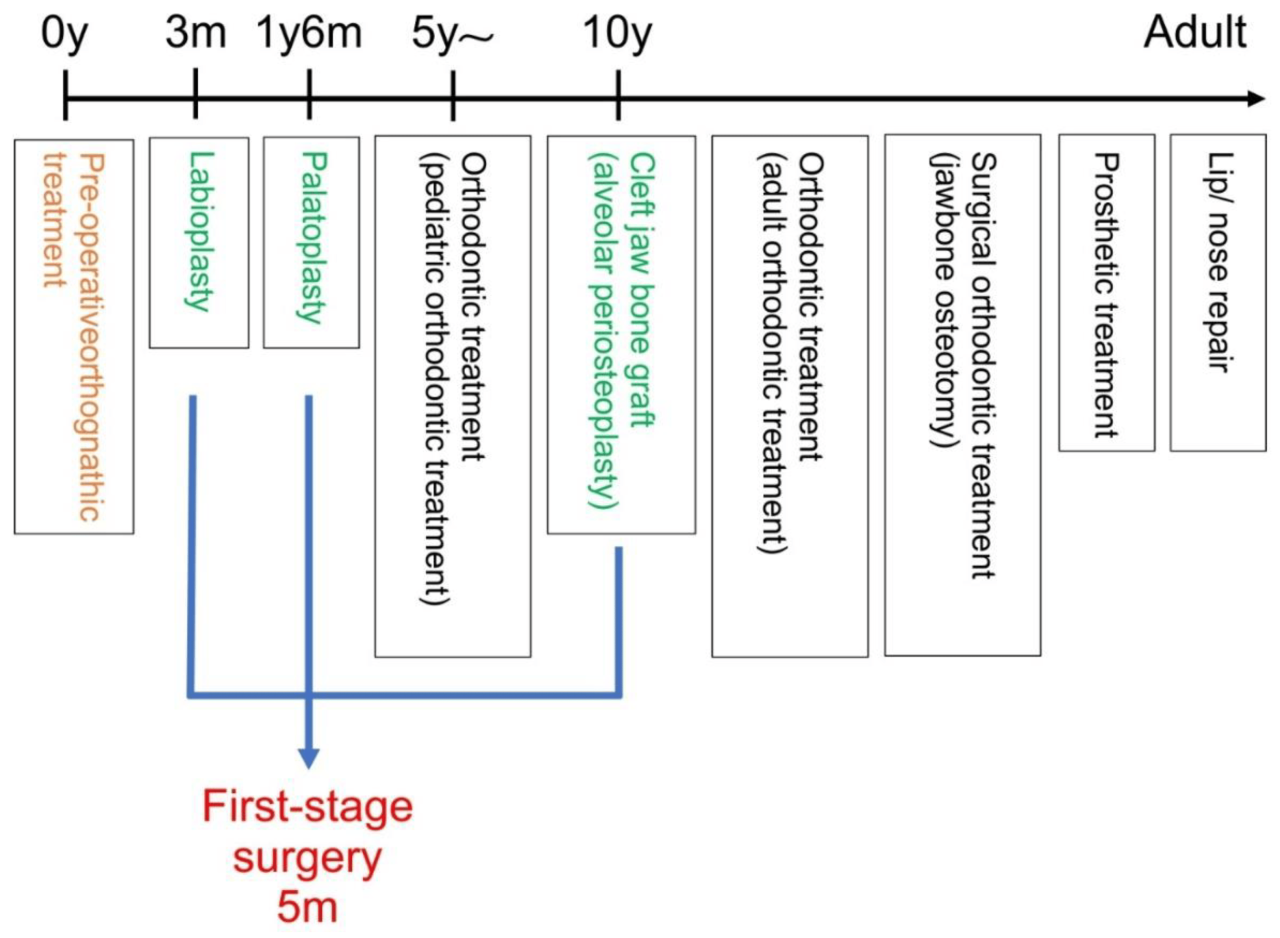
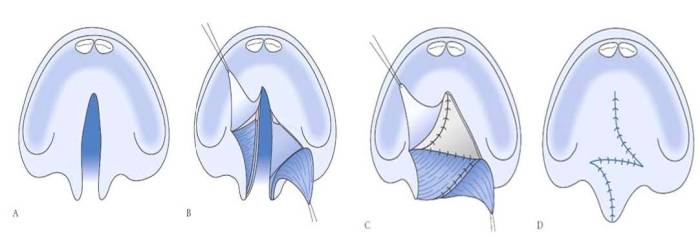
Surgical Techniques
Cleft lip repair involves various surgical techniques tailored to the severity and type of cleft. These techniques aim to restore lip function, improve aesthetics, and minimize scarring.
Classification of Techniques
Surgical techniques for cleft lip repair are broadly classified into two main approaches:
- Primary Repair:Performed in early infancy, typically within the first few months of life. It involves direct closure of the cleft without additional procedures.
- Secondary Repair:Conducted at a later stage, usually after 5 years of age, to refine the lip’s appearance and function. It may involve scar revision, nasal tip correction, or additional lip augmentation.
Primary Repair Techniques
Primary repair techniques include:
- Millard Technique:A popular method that involves rotating local flaps to close the cleft. It aims to preserve lip tissue and minimize scarring.
- Tennison-Randall Technique:Similar to the Millard technique, but uses a slightly different flap design. It is often used for wider clefts.
- Veau-Wardill-Kilner Technique:Involves using a flap from the nasal septum to close the cleft. It is suitable for clefts that extend into the nose.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The choice of surgical technique depends on factors such as the cleft’s severity, the patient’s age, and the surgeon’s experience.
Primary Repair:
- Advantages:Performed early, reducing the risk of speech and feeding problems. Minimizes scarring and provides a more natural lip appearance.
- Disadvantages:May require secondary procedures for refinement later in life.
Secondary Repair:
- Advantages:Allows for more precise refinement of the lip’s appearance and function. Can address residual scarring or asymmetry.
- Disadvantages:Performed later in life, which may impact the child’s emotional well-being. May involve more extensive surgery and a longer recovery time.
Post-Operative Care and Follow-Up
Post-operatively, patients require careful wound care, antibiotics, and pain management. Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor healing, ensure proper lip function, and address any complications.
Outcomes and Complications
Cleft lip repair is generally successful, with high rates of patient satisfaction and positive outcomes. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are potential complications that can occur.
Success Rates, Cleft lip repair cpt code
The success rate of cleft lip repair is high, with over 95% of patients achieving a satisfactory cosmetic result. The repair typically improves the child’s appearance, speech, and overall quality of life.
Complications
Potential complications associated with cleft lip repair include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Scarring
- Altered sensation in the lip
- Dental problems
- Speech problems
Managing and Preventing Complications
To manage and prevent complications, surgeons take several precautions:
- Using meticulous surgical techniques to minimize bleeding and scarring
- Prescribing antibiotics to prevent infection
- Using special dressings to protect the repair site
- Providing speech therapy to address any speech problems
- Monitoring the child’s progress closely for any signs of complications
Additional Considerations
Cleft lip repair has a profound impact on the patient’s quality of life, improving their physical appearance, speech, and social interactions. It can enhance their self-esteem and overall well-being.
Role of Multidisciplinary Teams
Cleft lip repair involves a team of specialists, including plastic surgeons, orthodontists, speech therapists, and psychologists. This multidisciplinary approach ensures comprehensive care, addressing all aspects of the patient’s needs.
Resources and Support Groups
Families affected by cleft lip can find support and resources through organizations like the Cleft Lip and Palate Association and the American Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Association. These groups provide information, support, and connect families with others who have experienced similar challenges.
Clarifying Questions
What is the CPT code for cleft lip repair?
The CPT code for cleft lip repair is 40820.
What are the components of the CPT code for cleft lip repair?
The CPT code for cleft lip repair consists of a five-digit code (40820) that identifies the specific procedure.
How is the CPT code used for billing cleft lip repair?
The CPT code is used to bill insurance companies for the cost of cleft lip repair.