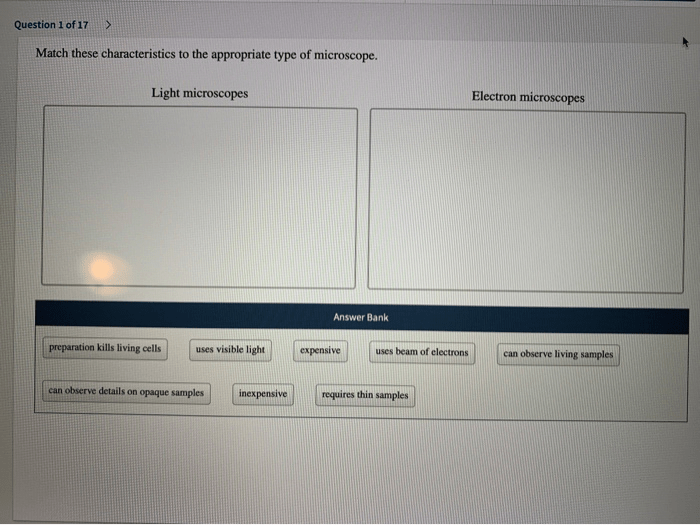
Match these characteristics to the appropriate type of microscope – As we delve into the realm of microscopy, the task of matching characteristics to the appropriate type of microscope takes center stage. This exploration will provide a comprehensive understanding of the diverse range of microscopes available, empowering researchers and practitioners alike to make informed choices based on their specific needs and applications.
The subsequent paragraphs will provide detailed descriptions of various microscope types, including their working principles, magnification ranges, resolutions, and applications. By understanding these characteristics and their alignment with different microscopy techniques, readers will gain a profound appreciation for the capabilities and limitations of each microscope type.
Introduction to Microscopy

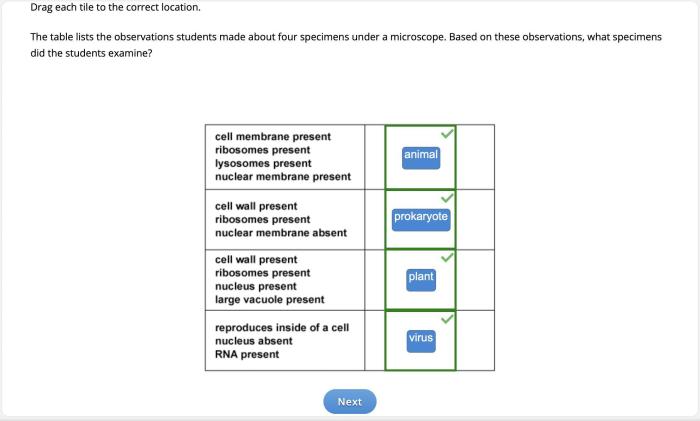
Microscopy is the technique of using microscopes to view objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Microscopes have revolutionized various fields, including biology, chemistry, medicine, and material science. A microscope is an instrument that produces magnified images of small objects.
It consists of lenses, a stage to hold the specimen, and a light source.
Types of Microscopes
There are various types of microscopes, each with its own principles, magnification range, and applications. Here is a table summarizing some common types:
| Type | Definition | Magnification Range | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Microscope | Uses visible light to illuminate the specimen | 10x
|
Biology, medicine, microbiology |
| Electron Microscope | Uses a beam of electrons to create an image | 100,000x
|
Materials science, nanotechnology |
| Fluorescence Microscope | Uses fluorescent dyes to highlight specific structures | 100x
|
Cell biology, immunology |
| Confocal Microscope | Uses a laser to scan the specimen and create a 3D image | 100x
|
Neuroscience, developmental biology |
Matching Characteristics to Microscope Types
Different microscopy techniques have specific characteristics related to sample preparation, imaging, resolution, and accessibility. Here is a list of characteristics and their corresponding microscope types:
- Sample Preparation:Light Microscope (least invasive), Electron Microscope (most invasive)
- Imaging Technique:Light Microscope (transmitted or reflected light), Electron Microscope (electron beam), Fluorescence Microscope (fluorescence), Confocal Microscope (laser scanning)
- Image Quality and Resolution:Electron Microscope (highest resolution), Light Microscope (lowest resolution)
- Cost and Accessibility:Light Microscope (most affordable and accessible), Electron Microscope (most expensive and specialized)
Applications and Limitations of Different Microscope Types: Match These Characteristics To The Appropriate Type Of Microscope
Each type of microscope has specific applications and limitations. Here are some examples:
- Light Microscope:Used for observing living cells, tissues, and microorganisms. Limited resolution for subcellular structures.
- Electron Microscope:Used for studying the ultrastructure of cells, viruses, and materials. High resolution but requires specialized sample preparation.
- Fluorescence Microscope:Used for visualizing specific molecules or proteins within cells. Limited penetration depth.
- Confocal Microscope:Used for creating 3D images of thick specimens. Can provide high-resolution images at different depths.
Future Trends in Microscopy
Microscopy is constantly evolving with new advancements and emerging technologies. Some promising trends include:
- Super-Resolution Microscopy:Techniques that break the diffraction limit of light microscopy, allowing for even higher resolution.
- Multimodal Microscopy:Combining different microscopy techniques to obtain complementary information from a single sample.
- Automated Microscopy:Using artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate image acquisition and analysis.
- Nanoscale Microscopy:Developing microscopes that can image objects at the nanoscale, opening up new possibilities in materials science and nanotechnology.
Top FAQs
What are the main types of microscopes?
The main types of microscopes include light microscopes, electron microscopes, fluorescence microscopes, and confocal microscopes.
What is the difference between magnification and resolution?
Magnification refers to the ability of a microscope to make an object appear larger, while resolution refers to the ability to distinguish between two closely spaced objects.
What factors should be considered when choosing a microscope?
Factors to consider when choosing a microscope include the type of sample being studied, the desired magnification and resolution, and the available budget.