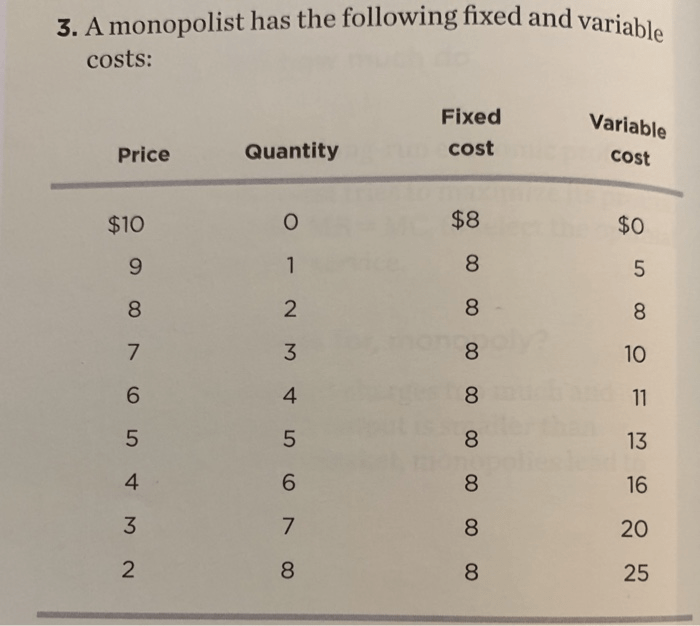
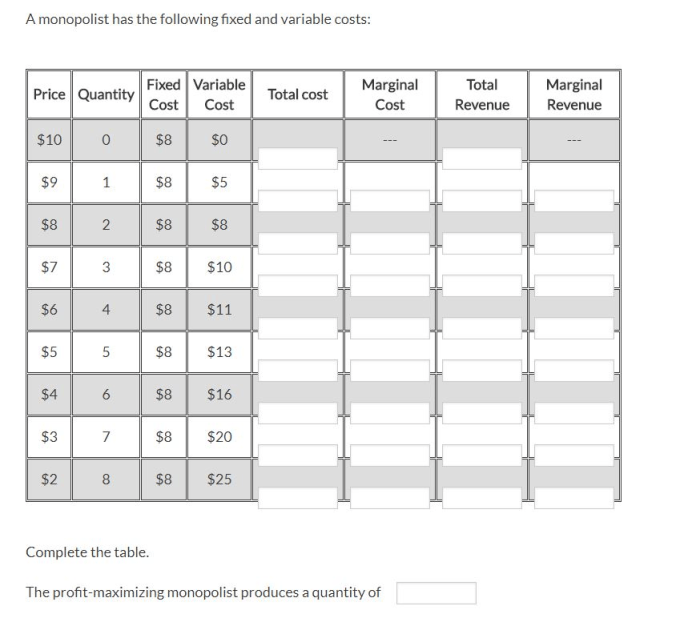
A monopolist has the following fixed and variable costs, which significantly impact its profit and market power. Understanding these costs is crucial for analyzing a monopolist’s behavior and the regulatory implications it faces.
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of output, while variable costs change with production levels. Marginal cost, the cost of producing one additional unit, plays a pivotal role in profit maximization. Monopolists seek to maximize profit by balancing these costs and setting output levels accordingly.
Fixed Costs
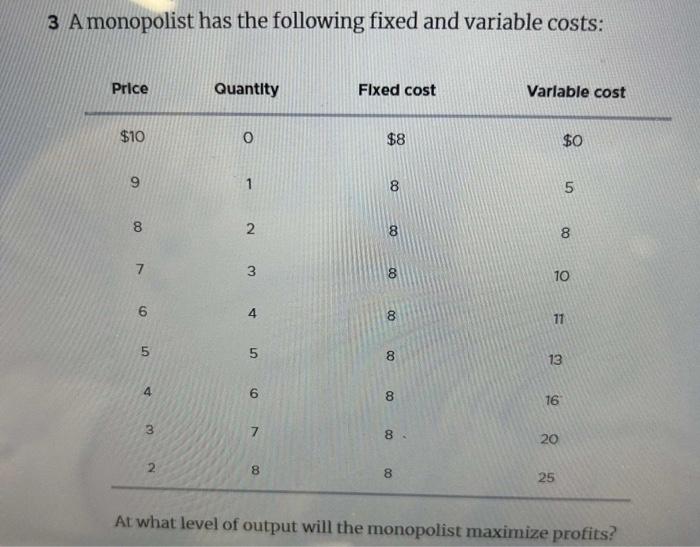
Fixed costs are costs that do not change with the level of output. They are incurred regardless of whether the monopolist produces any output or not. Examples of fixed costs include rent, property taxes, and salaries of managers.
Fixed costs can have a significant impact on a monopolist’s profit. If the monopolist has high fixed costs, it will need to produce a large amount of output in order to cover its costs and make a profit. This can lead to lower prices for consumers, as the monopolist tries to sell more output to cover its costs.
Variable Costs, A monopolist has the following fixed and variable costs
Variable costs are costs that change with the level of output. They are incurred only when the monopolist produces output. Examples of variable costs include the cost of raw materials, labor, and transportation.
Variable costs can also have a significant impact on a monopolist’s profit. If the monopolist has high variable costs, it will need to charge a higher price for its output in order to cover its costs and make a profit.
This can lead to higher prices for consumers.
Marginal Cost
Marginal cost is the cost of producing one additional unit of output. It is calculated by dividing the change in total cost by the change in output.
Marginal cost can be used to determine the monopolist’s profit-maximizing output. The monopolist will produce output up to the point where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
Profit Maximization
A monopolist maximizes profit by producing output up to the point where marginal cost equals marginal revenue. This is because at this point, the monopolist is producing the output that will generate the greatest amount of profit.
Fixed and variable costs play an important role in profit maximization. Fixed costs do not change with the level of output, so they do not affect the monopolist’s profit-maximizing output. Variable costs, on the other hand, do change with the level of output, so they can affect the monopolist’s profit-maximizing output.
Market Power: A Monopolist Has The Following Fixed And Variable Costs
Market power is the ability of a firm to influence the price of a good or service. Monopolists have market power because they are the only suppliers of a particular good or service.
The fixed and variable costs of a monopolist can affect its market power. If a monopolist has high fixed costs, it will be more difficult for it to enter the market. This is because the monopolist will need to charge a high price in order to cover its fixed costs.
This can make it difficult for new firms to enter the market and compete with the monopolist.
Regulation of Monopolies
Monopolies are often regulated because they can have negative effects on consumers. For example, monopolies can charge higher prices, produce lower-quality products, and reduce innovation.
There are a number of different methods that can be used to regulate monopolies. One method is to break up the monopoly into smaller firms. Another method is to regulate the prices that the monopolist can charge. A third method is to subsidize the production of competing firms.
FAQ Section
What are the main types of costs for a monopolist?
Fixed costs and variable costs are the two main types of costs for a monopolist.
How do fixed costs affect a monopolist’s profit?
Fixed costs do not vary with output, so they must be covered by revenue regardless of production levels. This can make it more difficult for a monopolist to earn a profit, especially in the short run.
How do variable costs affect a monopolist’s profit?
Variable costs vary with output, so they directly impact the marginal cost of production. A monopolist must consider variable costs when setting prices and output levels to maximize profit.